Virtual Private Networks (VPN) are hugely popular among companies and organizations that want to give their employees remote access to their private servers. By creating secure connections between remote nodes and your servers, VPNs solve some very important problems, such as preventing hackers from finding and breaking into your servers while enabling your employees to securely access their corporate files and applications from anywhere.
However, VPNs are not a perfect solution, and they are prone to specific security threats, such as phishing and spear phishing attacks. For instance, a hacker sends a legitimate-looking email to one of your employees and tricks them into installing a keylogger, a malware that records keystrokes and sends them to a remote server the hacker controls. All the attacker has to do is wait for the unsuspecting employee to type in her username and password.
Once in possession of valid credentials, the attacker will be able to connect to your VPN as a legitimate user, gain full access to your network, and steal information or cause other kinds of damage. This is the digital equivalent of a thief entering your store from the front door and robbing you blind in broad daylight.
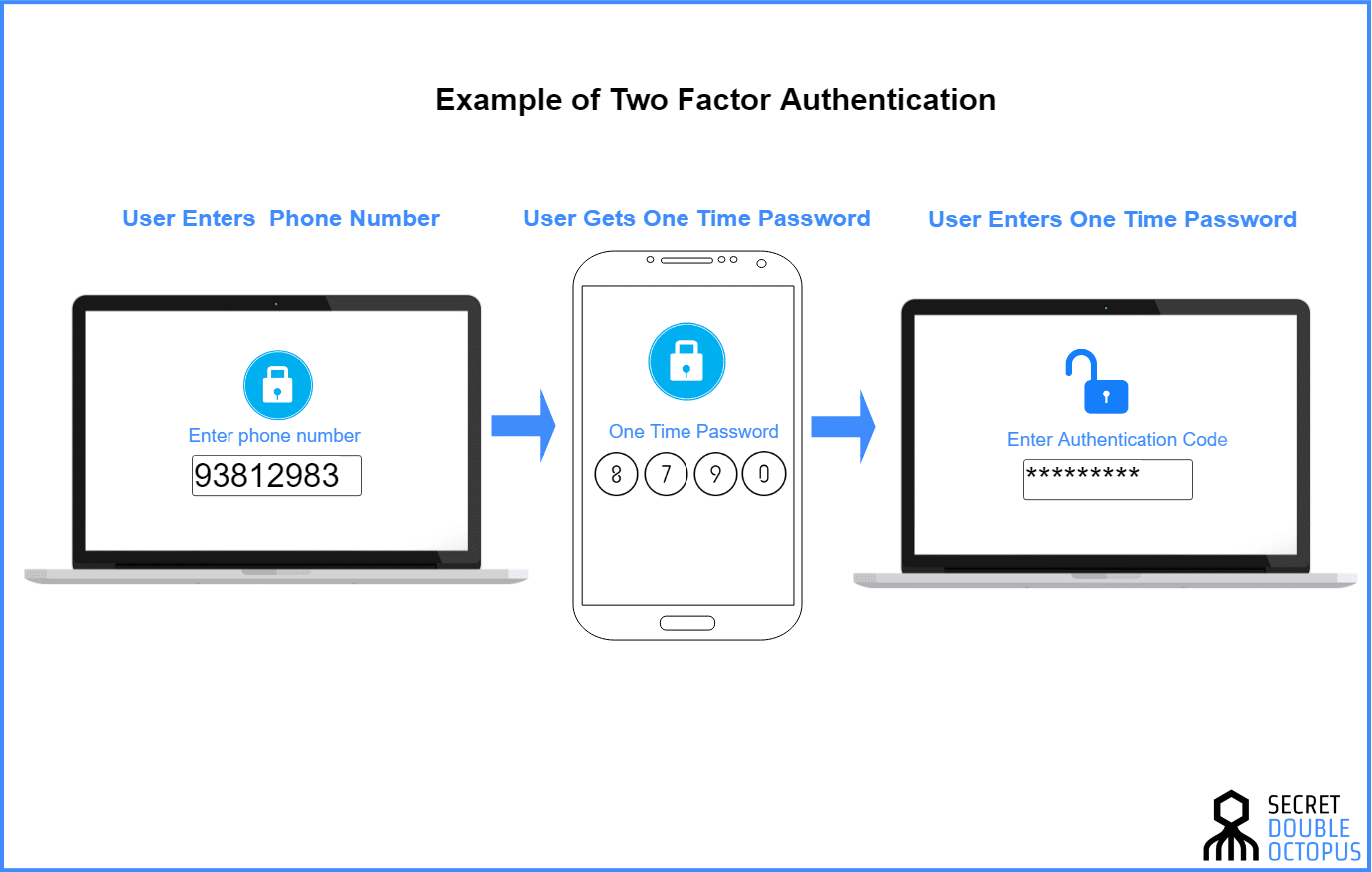
How two-factor authentication secures your VPN network
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a set of technologies that prevent intruders from accessing your network by stealing passwords. 2FA requires users to validate their identity and legitimate possession of credentials by presenting a second token in addition to their username and passwords. This can be a one-time passcode (OTP) or a time based one time password (TOTP) sent to an associated phone or mobile app, a fingerprint, or a physical key that generates unique cryptographic hashes.
One of the key ideas behind 2FA is that it is either impossible or extremely difficult to spoof or replicate it without physically accessing the token. Moreover, as it isn’t stored on any server, it is immune to data breaches. This means that even if hackers break into your servers and steal all the usernames and passwords of your employees, they still won’t be able to access your VPN because they don’t have the 2FA tokens.
VPNs are meant to give users access to your most sensitive digital assets, therefore hardening them with 2FA is a crucial step toward preventing hackers from gaining a foothold in the deepest recesses of your network.
How Secret Double Octopus makes 2FA more friendly and secure
One of the main criticisms against 2FA is its awkwardness and the fact that it requires the user to take additional steps — something that not all users appreciate. Moreover, not all 2FA technologies are equally secure and they each introduce their own complexities. SMS codes, for instance, are considered insecure, because they can be forwarded to a second phone that belongs to the hackers without the victim taking note.
Octopus Authenticator introduces a 2FA solution that is both secure and easy to use. Octopus does away with passwords and replaces them with the secure Authenticator app based on its proprietary keyless authentication platform. When installed on an employee’s mobile device, the Octopus Authenticator app will send them an access request notification each time someone tries to log into their VPN account, which they can either authorize (if it’s a legitimate attempt) or deny (if someone else is trying to access their account).
Despite its simple interface, Octopus Authenticator multi-factor authentication (MFA) for VPNs works some very sophisticated technology under the hood. Login attempts are secured through secret sharing algorithms distributed across several different channels, each with their own security mechanisms. While there’s no such thing as absolute security, it’s fair to say that with Secret Double Octopus, you get the best combination of security and user-friendliness.