What You Will Learn:
- Why phishing and compromised credentials remain leading attack vectors.
- The role of AI in increasing the sophistication of credential-based attacks.
- How passwordless MFA helps prevent credential-related breaches.
- The importance of Zero Trust identity strategies in stopping phishing attacks.
Executive Summary
The global average cost of data breaches continues to rise with phishing and compromised credentials serving as threat actors’ go-to attack vectors. In this post we’ll look at the increased risk, the changing role of user logins, and how companies can head off the majority of attacks by getting rid of passwords and weaving artificial intelligence (AI) deeper into their defenses.

Credentials maintain their appeal as initial attack vectors
The overall cost of suffering a data breach climbed 10% over the previous year reaching $4.88 million, the biggest jump since the height of the pandemic. And, for the second consecutive year, phishing and stolen or compromised credentials were the most prevalent attack vectors accounting for 15% and 16% of all breaches, respectively. These techniques also notched the second- and third-highest financial impact as the typical cost of a phishing-related breach hit $4.88 million and a breach involving compromised credentials averaged $4.81 million.

The speed and sophistication with which threat actors can build and execute social engineering, phishing, compromised credential and business email compromise (BEC) attacks all scale exponentially with the widespread adoption of AI making it easier for virtually anyone to devise believable pretexts and craft well-written, harder-to-detect phishing messages. This added sophistication appears to translate into greater difficulties detecting and resolving attacks. Breaches involving credential abuse took the longest to find and contain, along with attacks on employees and employee access in general.
Whether credentials were stolen or abused by malicious insiders, the time it took enterprises to identify and contain attacks increased:

Key factors that increased costs
According to the analysis by IBM and Ponemon, the top 3 factors that amplified breach costs were security system complexity, cyber skills shortages and third parties playing a role in data breaches.
Full recovery times exceeded 100 days
Skills shortages and the time that lapses before finding a breach also impact recovery and total cost. The longer it takes to find attacks, the more damage occurs that needs to be found and undone. More than three-quarters of organizations that had fully recovered said the process took longer than 100 days and one-third said recovery times topped 150 days.
Lack of skills a bigger factor than ever
More than half of breached organizations reported facing higher levels of security staffing shortages. Findings showed a 26.2% increase versus the prior year and that the corresponding average breach costs reached $1.76 million more. The perennial skills gaps widened quickly even as 1 in 5 organizations say they used some form of gen AI in security tools to boost productivity and efficiency.
New threats hiding in shadow data
An emerging threat, shadow data, drove the average cost of a data breach up to $5.27 million, 16.2% higher than the average. Breaches in which shadow data played a role also took 26.2% longer to find, which generally increases cost, and 20% longer – up to 291 days on average – to contain.
So how can you reduce the cost of a data breach?
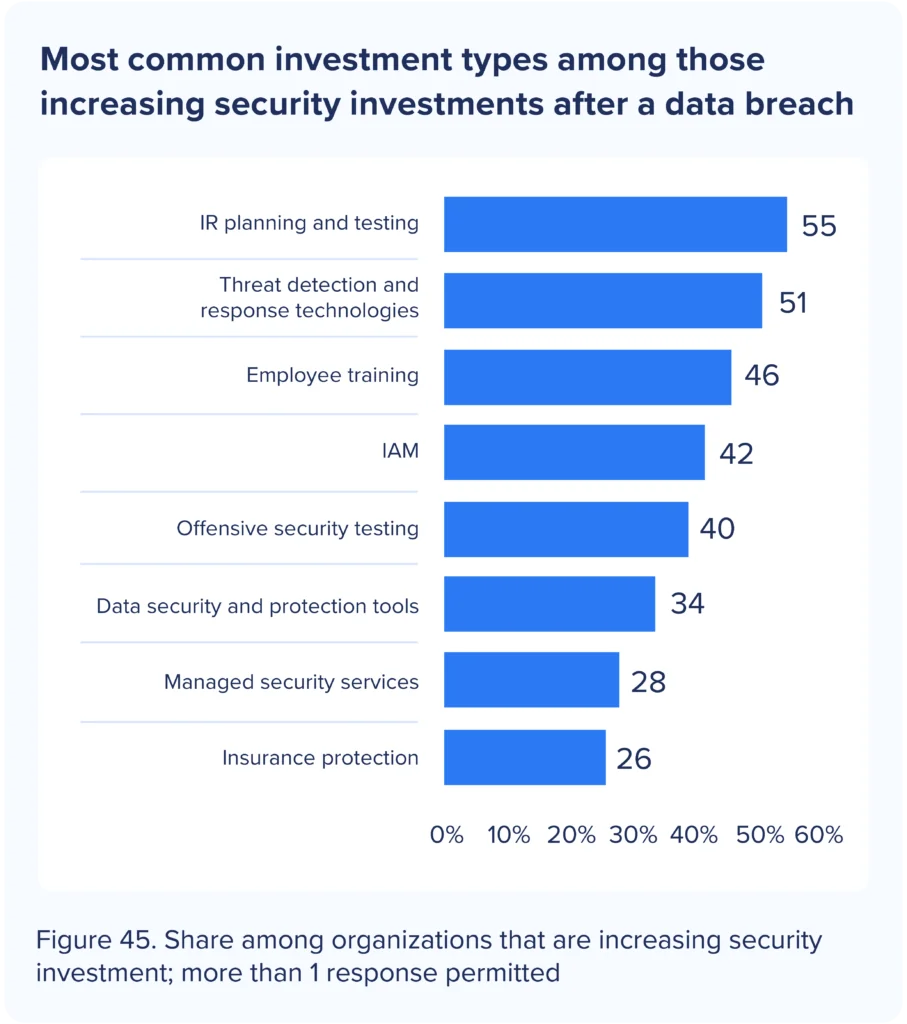
This year’s study found several factors — some predictable, some new — help to reduce the cost and minimize the damage done by data breaches. Employee training remains a top recommendation, particularly around recognizing the telltale signs of a social engineering or phishing attack. Organizations continue to invest heavily in trying to keep people –the perennial ‘weak link’ in the security chain — from allowing attacks to lead to breaches, whether it happens through accidentally revealing credentials, exposing privileged account data to open AI tools like ChatGPT, or deliberately leaking data, selling credentials, and colluding with third parties.
Education can’t go away, but it clearly hasn’t kept phishing from ranking high on the list of attack vectors year after year after year. Companies need to adopt smarter faster tools and phishing-resistant strategies, and the report findings show implementing AI and machine learning insights goes a long way. The most notable statistic shows that organizations using AI and automation extensively for security experienced average breach costs of $3.84 million while those that did not suffered losses averaging $5.72 mill ion — an added expense of $1.88 million per breach.
IAM ranks high on investment priority lists
While companies’ top priorities for increasing security investments included incident response and threat detection and response – in other words, dealing with threats after they get inside – training and identity and access management (IAM) attest to the interest and value of keeping threats out. IAM doesn’t just mean coming full circle back to the ‘castle-and-moat’ firewall-based approach of keeping outsiders out. It now means taking a forward-looking, Zero Trust approach that beings with proving workers and third parties are who they say they are.
A Zero Trust identity strategy becomes the foundational pillar of security best practices recommended by NIST, CISA, MITRE ATT&CK and other industry authorities. It basically means confirming identity beyond all reasonable doubt to block external, insider, and third-party threats, and finally put an end to phishing.
But how companies go about it matters.
Passwordless MFA puts a stop to phishing once and for all
Modern identity verification starts with multi-factor authentication (MFA) which usually asks individuals to complete a series of two or more steps like entering a password and then using a token, biometric, or one-time passcode (OTP) sent to their smartphone to complete the process. MFA has a big impact but any MFA that continues to use passwords as the first factor in authenticating workers leaves significant risk.
Passwords keep threat actors’ favorite attack vectors – human exploits like phishing and compromised credentials – alive in perpetuity. On the other hand, a passwordless MFA solution gets rid of the thing being phished and compromised, taking away the proverbial ‘keys to the kingdom.’
Removing passwords from your user login workflows literally removes the bait being targeted in social engineering attacks. Done right, a phishing-resistant passwordless login workflow:
- Eliminates 80% of organizations’ digital attack surface
- Makes workers up to 5% more productive
- Makes IT’s job easier (see why IT is the big winner)
- Saves an average organization up to $2 million per year (to run your own calculation, use our Passwordless ROI Calculator)
SDO’s approach closes skills gaps
Getting rid of passwords eliminates a lot of work for IT created by password rotations and Help Desk calls to perform account lockout resets. But in many cases, passwordless MFA takes a lot of time and effort to implement and support, and IT teams know this.
Secret Double Octopus (SDO) creates a faster, easier method of rolling out passwordless MFA that is compatible with your existing applications and identity infrastructure. With the Octopus, IT achieves 100% use case coverage quickly without inconveniencing users or burdening IT as does Windows Hello for Business (WHfB), a particle passwordless solution.

Our approach frees up IT and Help Desk professionals to tackle other strategic security initiatives, hunt for and respond to more threats faster, and streamline operations and administrative costs, all while moving closer to compliant Zero Trust cyber defenses.
Learn more about eliminating passwords to avoid breach costs
As long as passwords exist, phishing will exist. As the rise of AI making credentials a prime target, CISOs should consider how their companies can get rid of passwords quickly and easily to create strong, high-assurance authentication that stops phishing, ransomware, and huge financial losses due to data breaches in their tracks.
Key takeaways
- The cost of data breaches continues to rise with phishing and compromised credentials continuing to be primary attack vectors
- The rising use of AI by threat actors and perennial cyber skills shortages within enterprises play critical roles in increasing breach costs
- Zero Trust identity best practices that leverage passwordless MFA to confirm identity eliminate phishing and credential-based attacks while helping to bridge skills gaps
- SDO gives IT a faster, easier way to roll out and support passwordless MFA