Man-in-the-browser is a form of man-in-the-middle attack where an attacker is able to insert himself into the communications channel between two trusting parties by compromising a Web browser used by one of the parties, for the purpose of eavesdropping, data theft and/or session tampering.

Man-in-the-browser is often used by attackers to carry out various forms of financial fraud, typically by manipulating Internet Banking Services.
In order to compromise the browser, adversaries can take advantage of security vulnerabilities and/or manipulate inherent browser functionality to change content, modify behavior, and intercept information. Various forms of malware, most typically malware referred to as a Trojan horse, can be used to carry out the attack.
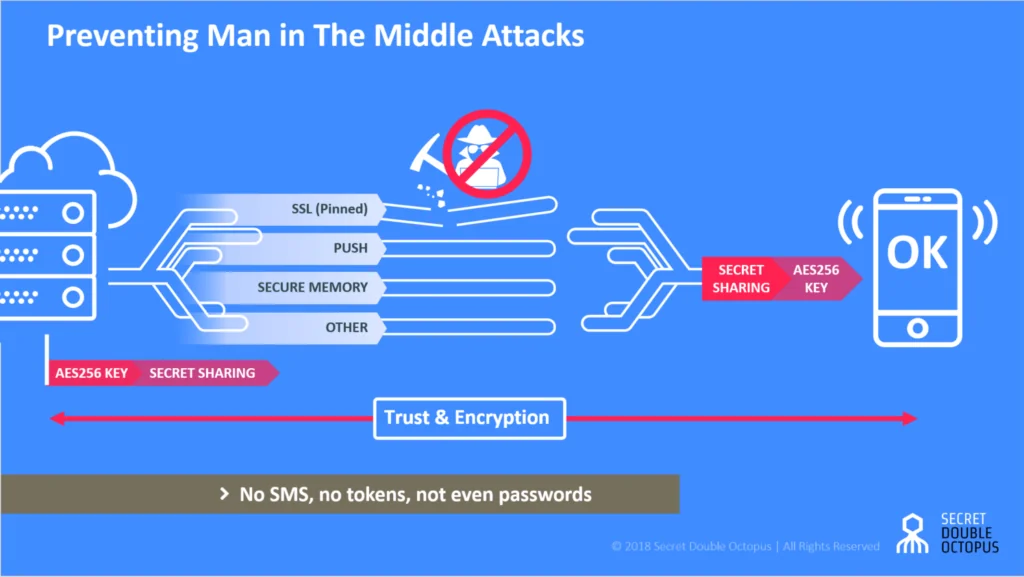
See Our Guide – Preventing Man in the Middle Attacks (MITB)